Neodymium, iron, boron, binding agents such as polyamide 11, 12 or PPS
Plastic-bonded, injected or pressed
See data sheets
Product
Plastic-bonded magnets, injected or pressed
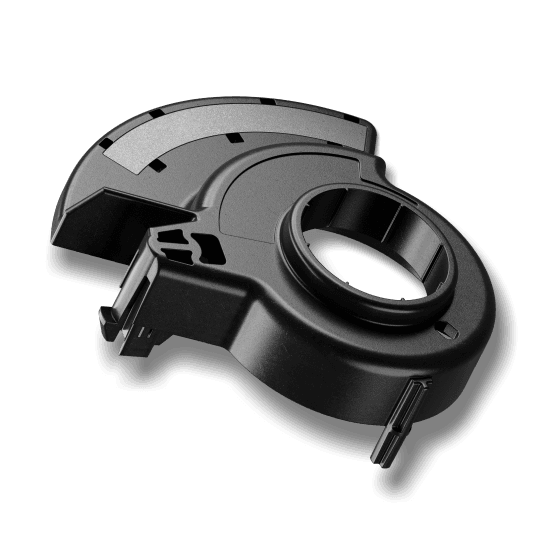
The magnetic compound is mixed from neodymium, iron, boron and a plastic granulate. The magnetic properties are determined by the proportion of rare-earth elements and the plastic used. Further processed in the injection molding process, a huge variety of shapes can be achieved, with very narrow tolerances. When processed through pressing, the magnet contains a higher proportion of NdFeB powder. As a result, higher magnetic properties are achieved than with injected neodymium magnets.
Huge variety of shapes
Insert parts such as bushings and shafts can be overmolded directly
No further processing necessary
General
Many shapes and levels of magnetization possible
Plastic-bonded NdFeB magnets offer a significantly higher magnetic performance compared to hard ferrites. This allows for much smaller and complex system configurations. Along with their complex shaping possibilites, they are mechanically durable, and their magnetization can be freely selected.
Chemical Resistance
Largely Resistant
Motor oil
Organic solvents
Conditionally Resistant
Uric acid < 10%
Not Resistant
Uric acid
Salts in aqueous solution
Acids and alkalis
Sea water
PRODUCTION PROCESS
Combined advantages
Plastic-bonded NdFeB magnets, created through the injection molding process, combine all the benefits of pure plastic injection molding with the fourth dimension – magnetism.
Note
The resistance to acids and alkalis depends on the plastic used. This needs to be checked for each specific application. Rare-earth magnets must be magnetized after the injection molding process using suitable magnetizing coils.
TECHNICAL DATA
What the plastic-bonded, injected NdFeB magnet can do
Plastic-bonded NdFeB magnets can be produced either by injection molding or pressing. This has an impact on their magnetization properties and the variety of shapes.
Bonded NdFeB compressed, isotropic
NdFeB injection molded, isotropic
Further Questions? Talk to an Expert!

